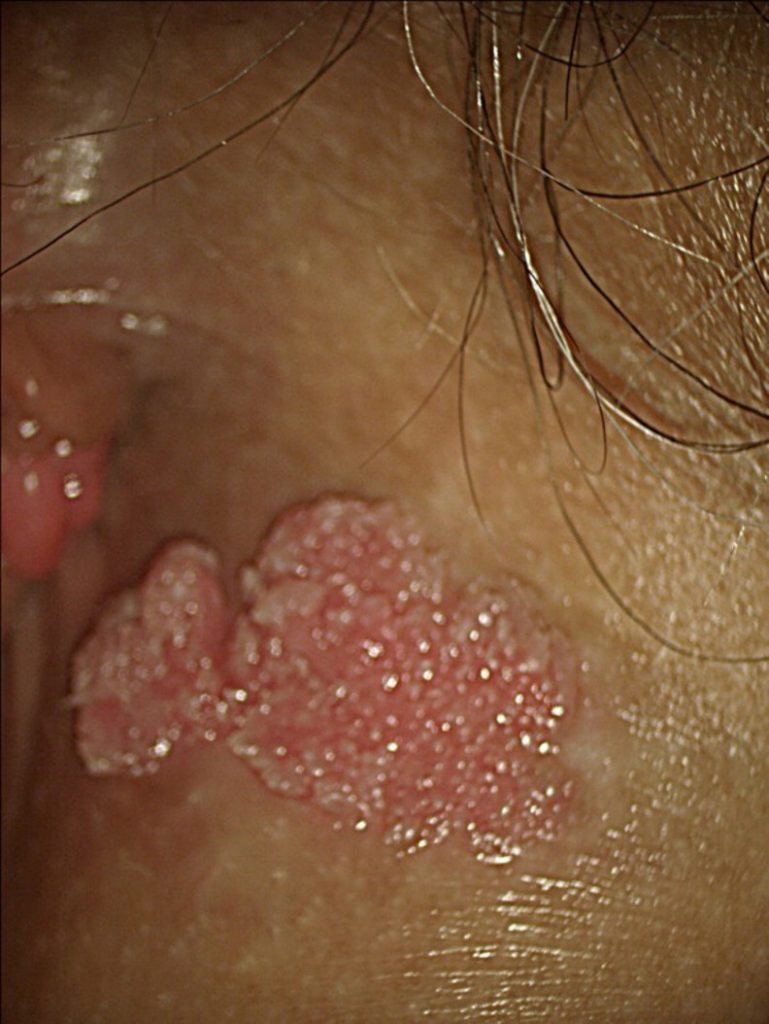
An in-depth look at external condylomata acuminata, commonly known as genital warts, is essential for understanding this prevalent sexually transmitted infection (STI). These small, flesh-colored or gray growths are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), a common virus that can spread through skin-to-skin contact during sexual activity.
External condylomata acuminata commonly present on the genitals, including the vulva, penis, scrotum, and anus. They can also occur in other areas where skin has come into contact with aninfected person, such as the inner thighs or buttocks. Symptoms may include itching, pain, or irritation at the site of the warts.
- Recognition of external condylomata acuminata is usually straightforward based on a visual examination by a healthcare professional.
- Management strategies for genital warts vary depending on the size, location, and number of warts.
Prevention of HPV transmission involves practicing safe sex, such as using condoms consistently and limiting the number of sexual partners. Vaccination against certain types of HPV is also available and can help protect against genital warts and other HPV-related diseases.
Understanding External Condylomata Acuminata
External condylomata acuminata, also known as genital warts, are small growths on the skin caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). These growths can appear in various areas of the body, particularly around the genitals, anus, or inner thighs. Contamination typically occurs through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, or oral intimacy. While many of HPV infections resolve on their own without causing any symptoms, some strains can lead to the development of condylomata acuminata. These warts are usually pinkish and may be raised. They can sometimes cause itching or pain.
- Manifestations of condylomata acuminata comprise small, flesh-colored growths on the skin.
- Diagnosis is typically based on a visual assessment by a healthcare professional.
- Therapy options vary depending on the size and location of the warts.
Is Condyloma Acuminata Treatable?
Condyloma acuminata, commonly known as genital warts, can be a sexually transmitted infection caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). While it is no cure for HPV itself, condyloma acuminata can often be completely resolved with various methods. Treatment options typically aim to remove the warts and reduce the risk of transmission.
Medical professionals may recommend a range of treatments depending on the size, location, and number of warts. These include topical medications like podophyllotoxin or imiquimod, cryotherapy (freezing), laser therapy, surgical excision, and electrocautery.
- This is important to note that even with successful treatment, HPV can remain in the body.
- Regular check-ups and screening for cervical cancer are crucial for individuals who have been detected with HPV.
- Vaccination against certain strains of HPV can help reduce the risk of developing condyloma acuminata and other related conditions.
HPV and Cancer Threat: Essential Information
Condyloma acuminata, referred to as genital warts, are small, smooth growths on the skin that are caused by certain strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV). While most people infected with HPV don't develop any symptoms, some individuals may experience these unpleasant growths in areas like the genitals, anus, or mouth. It's essential to understand that condyloma acuminata, while generally harmless on their own, can raise concerns about the risk of certain types of cancer.
Specifically, persistent infection with high-risk HPV strains is strongly linked to cervical cancer and other cancers of the reproductive system. Routine examinations are crucial for early detection and treatment of any potential precancerous lesions or cancerous growths. If you have concerns about condyloma acuminata or your risk of HPV-related cancers, it's important to consult with a healthcare professional.
The Association Between Condylomata Acuminata and Cervical Cancer
Condylomata acuminata, commonly known as genital warts, are/is/may be a sexually transmitted infection caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). Certain high-risk types of HPV can lead to precancerous changes in the cervix, which may eventually develop into cervical cancer. While not all individuals with condylomata acuminata will develop/experience/contract cervical cancer, there is/are/may be a clear link between these two conditions. Regular screening/testing/checkups, including Pap smears and HPV testing, are essential for early detection of precancerous changes and cervical cancer.
It's important to note that vaccination against high-risk HPV types can significantly here reduce the risk of developing both condylomata acuminata and cervical cancer.
Managing External Condylomata Acuminata: Symptoms and Diagnosis
External condylomata acuminata, commonly known as genital warts, are a raised bumps on the skin. These growths occur due to infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV), chiefly certain strains. The symptoms of condylomata acuminata can be itching, burning, or irritation in the affected area. In instances, warts could stay asymptomatic.
Diagnosis is typically made through a physical examination by a healthcare professional. They might inspect the genital area for any suspicious marks. A biopsy can occasionally recommended to verify the diagnosis and specify the specific HPV strain involved.
Effective Treatments for External Condylomata Acuminata
Treating these growths requires a tailored approach based on factors such as the extent of the lesions and the individual's medical history. Commonly prescribed treatments include topical medications like sinecatechins, which stimulate the immune system to target the wart virus. For larger or more resistant warts, laser treatment may be necessary. Regardless of the chosen method, it's essential to consult a physician for accurate diagnosis.
- Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor treatment results and address any complications that may arise.
- Beyond medical care, practicing good health habits can help prevent the spread of the genital wart virus.
Managing with External Condylomata Acuminata: Prevention and Care
Living having external condylomata acuminata can sometimes feel challenging. These small, painless, flesh-colored growths are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), and are frequently found in the genital area. While a majority of people disappear naturally, some may require medical attention.
Preventing condylomata acuminata centers around practicing safe sex by using condoms and getting the HPV vaccine. Should you suspect you have condylomata acuminata, it's important to consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment options.
- Refrain from sexual contact with infected individuals.
- Protect yourself by getting the HPV vaccine. It's best at protecting against certain types of HPV that can cause condylomata acuminata and other health issues.
Despite the fact that there is no cure for HPV, treatment options can be implemented to remove or reduce the appearance of condylomata acuminata. These include freezing, laser surgery, and topical medications.
Might Condylomata Acuminata Transfer?
Genital warts, medically known as condylomata acuminata, are a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). These small, flesh-colored bumps can appear on various areas of the vulva and {may{ spread through direct skin-to-skin contact during sexual activity. It's crucial to understand that HPV can be transmitted even without visible warts being present.
Understanding the Value of Early Detection and Treatment of Condylomata Acuminata
Early detection and treatment are crucial for effectively managing condylomata acuminata. These lesions, caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), can sometimes be asymptomatic, making regular checks essential. When detected early, condylomata acuminata can often be successfully treated with topical medications or minor surgical procedures. This minimizes the risk of complications and helps prevent the spread of HPV to uninfected regions of the body. Reaching out a healthcare professional for any unusual changes in the genital area is crucial for ensuring timely diagnosis and treatment.
Genital Warts FAQs
External condylomata acuminata, also known as genital warts, are small, flesh-colored bumps that can develop on the skin surface. They are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), a common virus that can be transmitted through sexual contact.
It's important to remember that not everyone infected with HPV will develop warts. Some people may have no symptoms at all, while others may only experience mild discomfort or irritation.
- What are the signs of genital warts?
- How can I manage genital warts without medical intervention?
- Can vaccination against HPV reduce the risk of developing condylomata acuminata?
If you suspect you may have external condylomata acuminata, it's essential to see a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment. Early detection and intervention can help manage the condition and prevent complications.